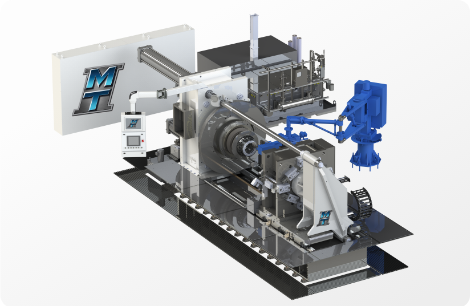
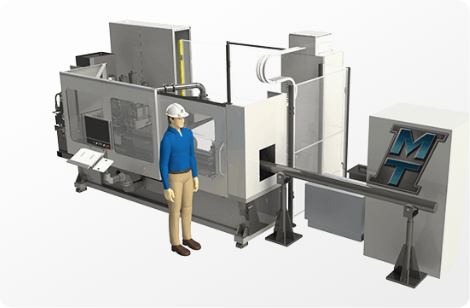
Structural Integrity for Maximum Efficiency of
Pre-Fabricated Components
Friction Welding for Construction and Agriculture Applications
Increase Machine Durability and Decrease Wear
For over 40 years, MTI has been the global expert in friction welding technology. We build friction welders for manufacturers seeking a product line for structural and machinery components. Furthermore, we also operate our own line of in-house welders to produce and innovate with engineers.
Agriculture and construction share the same goal. Structural integrity differs between a robust, reliable structure and one that fails under stress. MTI is here to offer flexible and creative solutions for the unique needs of these industries.
MTI Model 60T Rotary friction welder demonstration joining hydraulic cylinder rods.
Advantages & Benefits
Building Strength in Construction and Agriculture
MTI’s friction welding solutions are revolutionizing the construction and agriculture industries. Our advanced technologies deliver superior quality, efficiency, and sustainability, empowering manufacturers to create more durable and eco-friendly equipment.
Forged Quality
As friction welding creates a 100% solid-state bond as opposed to traditional welding processes, the end product is of forged quality. This results in a longer useful life span and reduces wear and tear after excessive use, contributing to savings on your bottom line. The end result is a product that retains most if not all parent material properties, a bond strong enough to handle the stress and torque required of heavy machinery components.
Machine-controlled Process
The construction and agriculture industry require high precision and quality components. Friction welding ensures consistent, high-quality welds with minimal human error, enhancing the durability and reliability of equipment. This automation improves production efficiency and reduces labor costs. It also increases safety by reducing the need for manual welding in potentially hazardous environments.
Green Technology
Friction welding is an eco-friendly technology that does not emit smoke, fumes, or gases. Friction welding does not require consumables such as flux or filler material, reducing your carbon footprint all the way down your supply chain as less material and energy is used.
As friction welding creates a 100% solid-state bond as opposed to traditional welding processes, the end product is of forged quality. This results in a longer useful life span and reduces wear and tear after excessive use, contributing to savings on your bottom line. The end result is a product that retains most if not all parent material properties, a bond strong enough to handle the stress and torque required of heavy machinery components.
The construction and agriculture industry require high precision and quality components. Friction welding ensures consistent, high-quality welds with minimal human error, enhancing the durability and reliability of equipment. This automation improves production efficiency and reduces labor costs. It also increases safety by reducing the need for manual welding in potentially hazardous environments.
Friction welding is an eco-friendly technology that does not emit smoke, fumes, or gases. Friction welding does not require consumables such as flux or filler material, reducing your carbon footprint all the way down your supply chain as less material and energy is used.
Our Commitment
Excellence in Every Weld, Perfection in Every Detail
MTI brings the highest possible degree of safety and quality, whether it’s a part we’re welding or a machine we’re building. We are equipped to produce parts for the most sensitive environments and exacting standards.
Friction Welding Machines for Agriculture and Construction
Consistent quality welds are crucial in agriculture and construction. For example, a butt joint must have a weld of 100% contact area to handle the high stress of torque. This is essential for components in irrigation systems and construction machinery.
Friction welding ensures a full surface weld of superior strength even if materials are not conventionally compatible for welding through other methods. And with automation for your friction welding machine, quality is consistent from the first part to the last. MTI is a leading manufacturer of such machines and services worldwide.
Friction Welding Machines for Agriculture and Construction
Consistent quality welds are crucial in agriculture and construction. For example, a butt joint must have a weld of 100% contact area to handle the high stress of torque. This is essential for components in irrigation systems and construction machinery.
Friction welding ensures a full surface weld of superior strength even if materials are not conventionally compatible for welding through other methods. And with automation for your friction welding machine, quality is consistent from the first part to the last. MTI is a leading manufacturer of such machines and services worldwide.
ROTARY FRICTION WELDING
MTI specializes in all forms of rotary friction welding: Direct Drive, Inertia, and Hybrid.
LOW FORCE FRICTION WELDING
Need to eliminate flash removal? Our Low Force friction welding machines reduce the amount of material lost during the weld.
FRICTION STIR WELDING
This form of friction welding is ideal for panels. Our large panel production machine has dual upper and lower weld heads for faster welding.
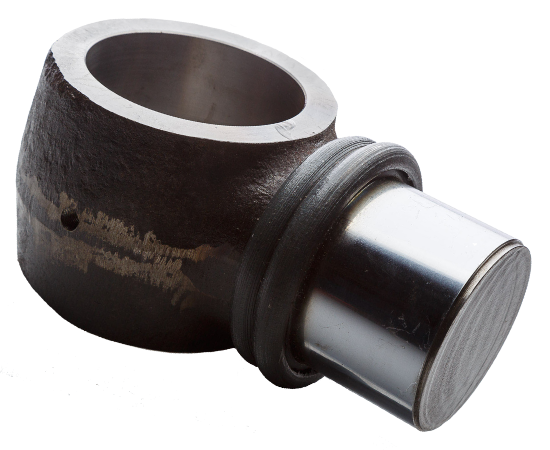

Explore Our Sample Parts
Our geometry sample parts have a story behind them, guiding you closer to innovation. Discover new ideas that are applicable to making your new project possible.
Contract Manufacturing Services
When you partner with us to build and design a friction welding machine or parts big and small, we provide the expertise and tools to make it possible. From specs to development to production, we are committed to your success.
Contract Manufacturing Services
When you partner with us to build and design a friction welding machine or parts big and small, we provide the expertise and tools to make it possible. From specs to development to production, we are committed to your success.
Construction and Agriculture Friction Welding Machines for R&D
We have the machines to help you innovate.
Friction welding methods work differently for many materials. Our in-house friction welding machines allow you to test the different bi-metallic combinations you need for your next project.
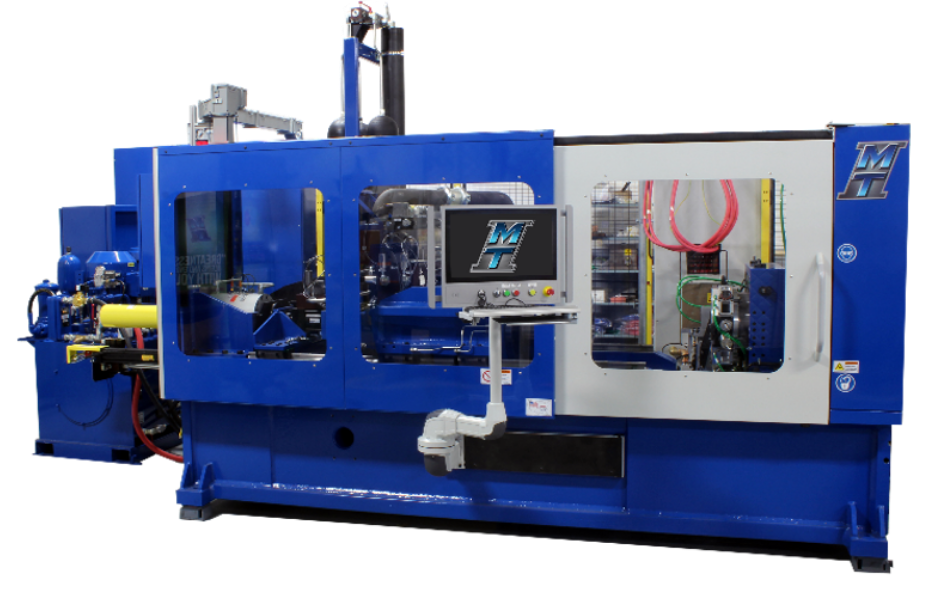

Low Force Rotary Lab Machine
Learning Center
Featured Articles
Case Studies
Videos
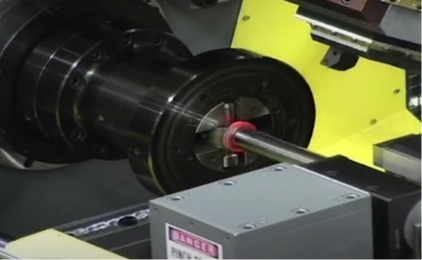
Construction & Agriculture Video

Construction & Agriculture Video
Get the information you need, before you need it — free and straight to your inbox from industry experts.