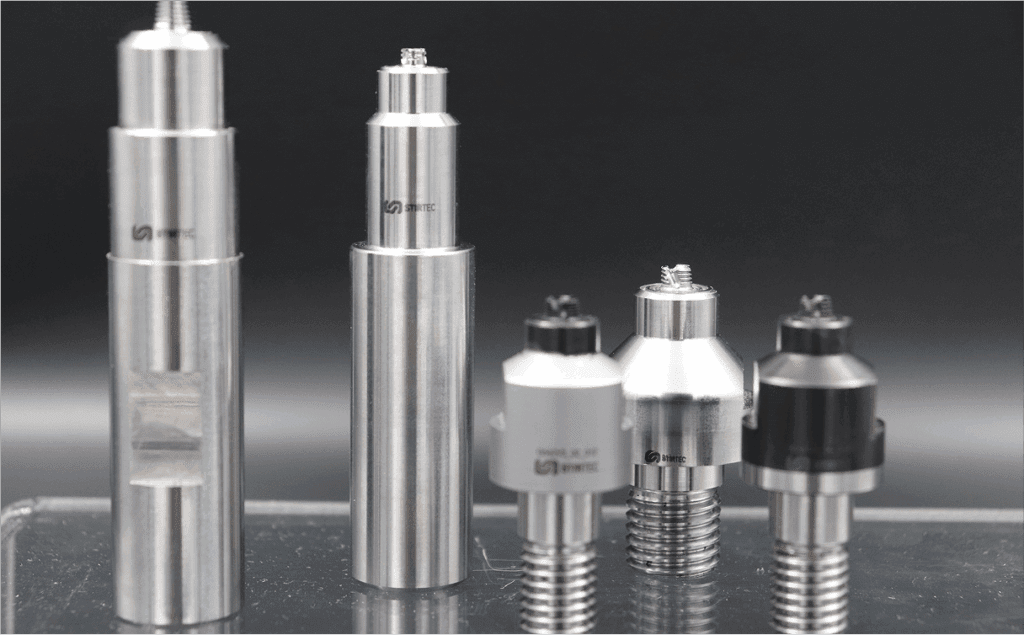
FSW Tool Materials
Understanding the Role of Tool Materials in Friction Stir Welding
Materials are one of the several variables that factor in to the development of FSW tools. It’s a critical step in achieving strong, high-quality welds tailored to your specific production needs with expert guidance. The material properties of FSW tools directly influence wear resistance, heat tolerance, and overall tool life, particularly when joining challenging alloys such as titanium or stainless steel.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most common and advanced FSW tool materials, outlining their strengths and ideal use cases to enlighten you on the best fit for your manufacturing and automated welding processes.
Common Materials Used
in FSW Tools
The selection of appropriate materials for FSW tools is critical to their performance and durability. The demands placed on the tool—in terms of strength, hardness, wear resistance, and thermal properties at elevated temperatures—vary significantly depending on the material being welded.
Tool Steels
AISI H13 and Similar Hot-Work Tool Steels:
- Widely used for welding aluminum alloys
- Offer good strength, machinability, and thermal fatigue resistance
- Operate effectively at the lower temperatures involved in aluminum welding
- Cost-effective for many common applications
High-Speed Steels (HSS)
- Provide a good balance of hardness and toughness
- Suitable for aluminum alloys
- Better wear resistance than standard tool steels
- Maintain hardness at moderately elevated temperatures
Nickel and Cobalt Superalloys
- MP159, Nimonic alloys, and similar materials
- Cobalt and nickel-based alloy FSW tools offer excellent strength at elevated temperatures
- Suitable for higher strength aluminum alloys
- More expensive than tool steels
- May have lower toughness in some applications
Tungsten Carbide (WC)
- High strength and exceptional wear resistance
- Appropriate for abrasive materials like aluminum castings containing silicon
- Well-suited for copper alloys
- Potential limitations in toughness at lower temperatures
- Often used in composite tools or as inserts
Tungsten Heavy Alloys
- Particularly effective for copper welding
- Good combination of strength and thermal conductivity
- More expensive than conventional tool materials
Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN)
- PCBN FSW tools have excellent hardness and strength at high temperatures
- Ideal for welding hard materials like steels and titanium alloys
- Very high wear resistance
- Significantly more expensive than metallic tool materials
- Limited availability in complex geometries
Ceramics
- Advanced ceramics
- High wear and heat resistance
- Suitable for thick plates of ferrous metals
- Provide a cost-effective alternative to PCBN
- May be more brittle than metallic options
Refractory Metals and Alloys
- Tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, and their alloys
- Used for high-temperature applications (titanium, steels)
- Often alloyed to enhance strength and durability
- Lanthanated tungsten preferred for titanium alloys

Access Your FSW Tool Guide
Gain insights into the other variables that influence the design of the right FSW tool.
Material Selection Considerations
The choice of tool material involves balancing several factors:
- Temperature Resistance: Must withstand the peak temperatures generated during welding.
- Wear Resistance: Particularly important for abrasive materials and long production runs.
- Strength and Toughness: Essential to prevent tool failure under the forces involved.
- Chemical Compatibility: Must not react adversely with the workpiece material.
- Cost and Availability: Practical considerations for industrial applications.
The ongoing trend in FSW tool material development focuses on creating harder and more heat-resistant materials to expand the process’s applicability to a broader range of high-performance alloys. Research into new tool materials continues, with interest in intermetallic alloys, silicides, Laves phase alloys, and other advanced materials that might offer improved performance or lower cost.
Through the engineering expertise of MTI and STIRTEC, you can access the latest materials available to design your FSW tool for the fastest and most durable welds.
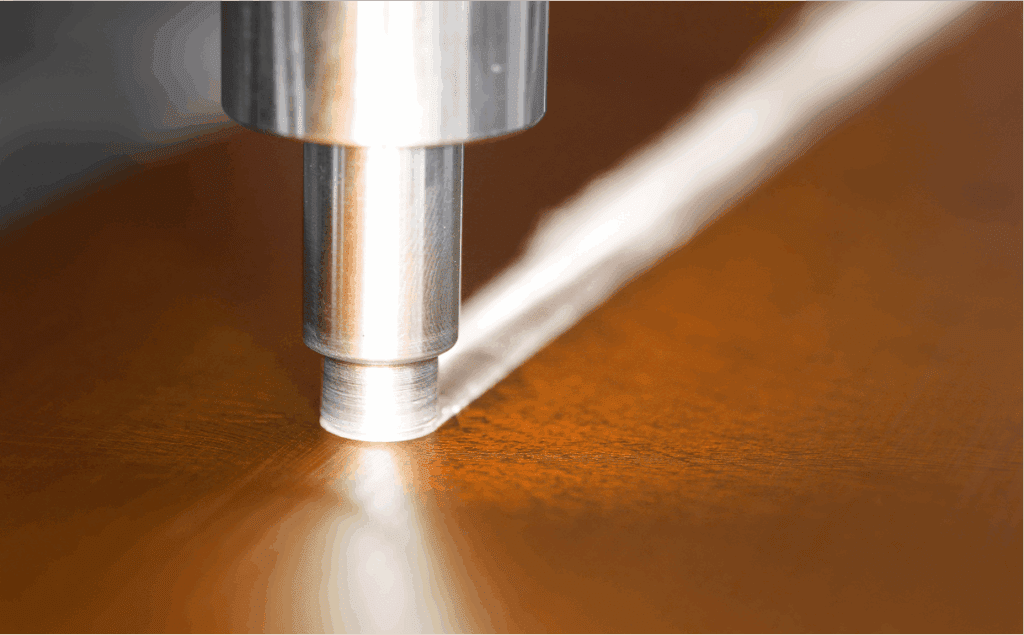
Get Expert Guidance on FSW Tooling
Selecting the right FSW tool materials is essential for achieving high-performance welds with the proper wear resistance, heat tolerance, and durability for the application that they are designed for.
Understanding standard and advanced FSW tool materials is crucial for designing a tool tailored to your organization’s needs. However, it is only one of the many variables for FSW tool design in achieving the productivity, extended tool life, and support you need for your automated welding process.
Need expert guidance beyond our downloadable guide? Speak with an FSW expert today. As a global leader in solid-state joining solutions, we offer full-service FSW development support—from material selection to tool design and production needs.
Everything You Should Know About Friction Stir Welding Tools
Get clear, expert-driven answers to common questions about FSW tool selection, including guidance on tool materials, configurations, and application-specific solutions.
Get the information you need, before you need it — free and straight to your inbox from industry experts.